
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Treatment Options
Your child may suffer from Obstructive Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (OETD), a common form of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD).2

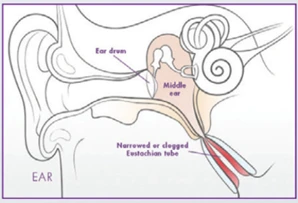
The Eustachian tube is a narrow tube linked to the middle ear. It is normally closed but opens when we swallow, yawn or chew.3 As the Eustachian tube opens and closes, it regulates pressure in the ear. ETD is the failure of the valve of the eustachian tube to open and/or close properly.4
Ear tubes are one of the current therapies to treat OETD.5 The recurrence rate following ear tube insertion is high and a study showed that the mean time for ear tube to fall out varies from 7 - 14 months.6 If your child requires another set of tubes, a new path to treat the source of your child’s OETD is available now!*
How Does It Work?
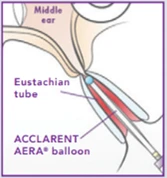
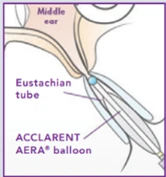
The ACCLARENT AERA® Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation System device is a small balloon that is inserted through the nose into the Eustachian tube.
The ACCLARENT AERA balloon in inflated for 2 minutes which dilates the Eustachian tube and may relieve ETD symptoms.
After the balloon is inflated and the Eustachian tube is dilated, the doctor deflates and removes the balloon.
Proven efficacy – Evidence shows that ETBD with ACCLARENT AERA is comparable to ear tube placement alone
Evidence shows that ETBD with ACCLARENT AERA is comparable to ear tube placement alone.
Ask your doctor if this alternative is suitable to treat your child’s ear health.

Please Note: The Find your Doctor locator ("Locator") provided here is intended for use by the general public as a quick reference for patients wanting to locate physicians who perform procedures with the Acclarent portfolio. Integra LifeSciences and its parents, subsidiaries, affiliates, directors, officers, employees, agents, and representatives (collectively "Integra") does not, in anyway, endorse the individuals, institutions or group practices included in the Locator. Similarly, any omission from the Locator does not suggest disapproval or any other position or assessment by Integra.
Disclaimer: The information featured here is not intended as medical advice, or to be used for medical diagnosis or treatment. Please talk to your doctor if you have questions. This content is intended for audience within the US only.
References
- Traditional 510(k): Device Labeling Modification to ACCLARENT AERA(R) Eustachian Tube Balloon System, (K230742), cleared December 13, 2023.
- Stanford Medicine Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction webpage accessed 1/24/2024. https://med.stanford.edu/ohns/OHNS-healthcare/earinstitute/conditions-and-services/conditions/eustachian-tubedysfunction.html.
- Llewellyn A, Norman G, Harden M, et al. Interventions for adult Eustachian tube dysfunction: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(46):1-vi.
- Johns Hopkins Medicine. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction webpage accessed 1/24/2024. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditionsand-diseases/eustachian-tube-dysfunction.
- Cleveland Clinic. Tympanostomy (Ear Tubes) webpage accessed 1/24/2024. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/15609-eartubes-tympanostomy.
- Alaraifi AK, Alkhaldi AS, Ababtain IS, Alsaab FA. Predictors of tympanostomy tube extrusion time in otitis media with effusion. Saudi Med J. 2022 Jul;43(7):730-734.
- Howard A, Babu S, Haupert M, Thottam P Balloon Eustachian Tuboplasty in pediatric patients: is it safe? Laryngoscope, 131:1657-1662, 2021 doi:10.1002/lary.29241.
*84% of ears were failure-free after a mean of 2.7 years of follow-up (failure was defined as whether further surgery was needed to treat the patient’s ETD, e.g., ear tubes or revision ETBD)
**Sample size – 20 patients aged 8-17 with chronic otitis media with effusion
***A serious adverse event is any adverse event that: 1) Results in death, 2) Is lifethreatening or places the participant at immediate risk of death from the event as it occurred, 3) Requires or prolongs hospitalization, 4) Causes persistent or significant disability or incapacity.
†Reported adverse events have included epistaxis and transient otalgia in rare instances